Along with growing progressive analysis applications, life science analysis school at research-intensive establishments are tasked with offering profession mentoring and scientific coaching to new generations of scientists, together with postgraduate, graduate, and undergraduate college students.
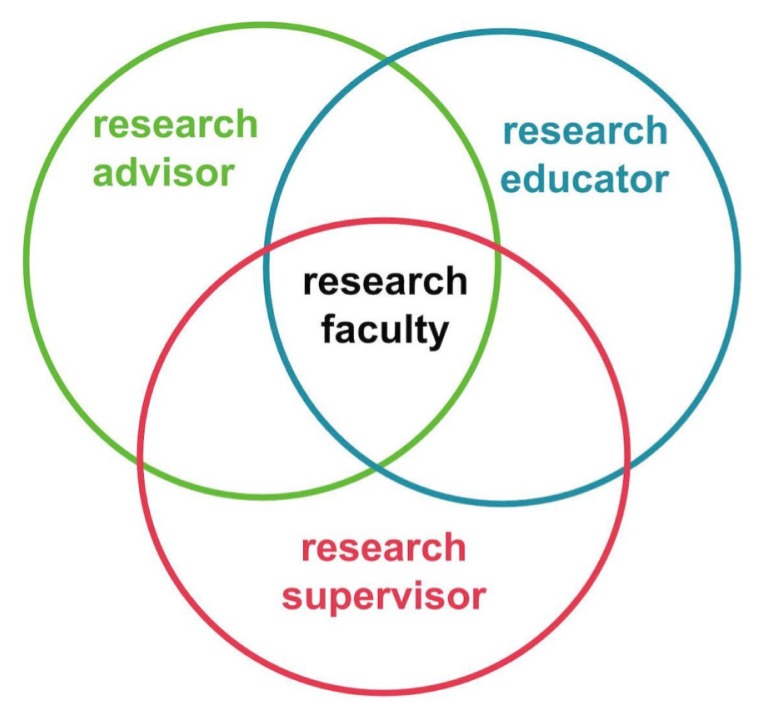
On this essay, we argue for a redefinition of mentoring in laboratory analysis, to totally distinguish three important roles performed by analysis school relative to their trainees: advisor, educator, and supervisor.
Particularly, we take note of the usually unacknowledged and misunderstood function of a school member as a supervisor and focus on the impression of neglecting supervisory finest practices on trainees, on the variety of the educational pipeline, and on the analysis enterprise. We additionally present actionable frameworks for analysis mentors who want to use inclusive supervisory and pedagogical practices of their laboratory.
Lastly, we name for extra analysis across the supervisory function of analysis school and its impression on trainees, notably neighborhood faculty college students, so as to assist broaden the participation of underrepresented college students in STEM fields.
The science commons in life science analysis: construction, operate, and worth of entry to genetic range.
Innovation within the life sciences will depend on how a lot data is produced in addition to how extensively and simply it’s shared. Insurance policies governing the science commons – or various, extra restricted informational areas – decide how extensively and shortly data is distributed.
The aim of this paper is to focus on why the science commons issues and to analyse its construction and performance.
The primary lesson from our evaluation is that each the traits of the bodily sources (from genes to microbes, vegetation and animals) and the norms and beliefs of the totally different analysis communities – consider the Bermuda guidelines within the human genome case or the Belem declaration for bioprospecting – matter within the institutional selections made when organising the science commons.
We additionally present that the science commons contributes to fixing a few of the collective motion dilemmas that come up within the manufacturing of information in Pasteur’s Quadrant, when data is each scientifically necessary and virtually relevant.
We present the significance of two of those dilemmas for the life sciences, which we name respectively the diffusion-innovation dilemma (how readily innovation diffuses) and the exploration-exploitation dilemma (when software requires collective motion).
